Aspect-Oriented Instrumentation with GCC
Brief history of GCC
Started as GNU project's C compiler in 1985.
The EGCS project merged several forks including supports for Fortran, C++.
In April 1999, EGCS took over mantainership of GCC.
Known as the GCC steering committee.
Generally
speaking, committee members were chosen to represent
the interests of communities (e.g. Fortran users,
embedded systems developers, kernel hackers), not
companies.
GCC Plugin
Plugin support released in April 2010.
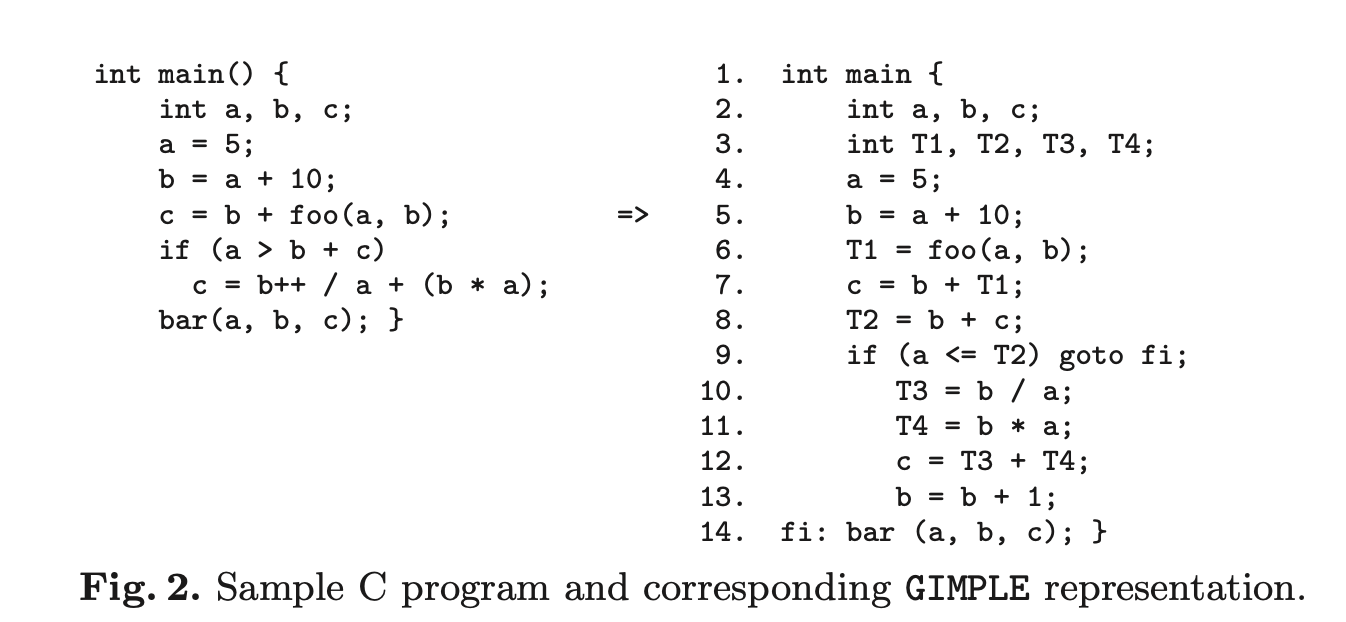
Working with a three address code IR format, GIMPLE
GIMPLE is independent of frontend languages, so plugins can be used with C, C++, Fortran, Java(?), Ada, etc.
A plugin need not only provide optimization passes but also analysis tools.
GIMPLE
- Making up GCC's middle-end
- Does not have textual syntax
- Need's to be manipulated using API
- Preserves source-level function calls and data types.
What problem does InterAspect trying to solve?
The interface provided by GCC via GIMPLE is too low-level, need more abstraction to make GCC plugin writing easier for tasks like code instrumenting.
The framework itself can maybe used to implement AOP extension to languages supported by GCC.
Aspect Oriented Programming
Terminology
- Join points:
- Where the call to advice functions could be injected.
- Pointcuts:
- Specifiers how to match join points.
- Advice functions:
- Snippets of codes that can be injected to join points.
- Weaving:
- The process that inserts calls to advice functions.
Aspect J Examples
Pointcuts: match method calls that has name
start with set from object of type Point
pointcut set() : execution(* set*(..) ) && this(Point);
Advices: Add code after the set() pointcut.
after () : set() {
Display.update();
}
What InterAspect does
Traverse the GIMPLE representation and calls user defined callback functions on join points matched by pointcuts, to determine what advice functions would be inserted at each join point.
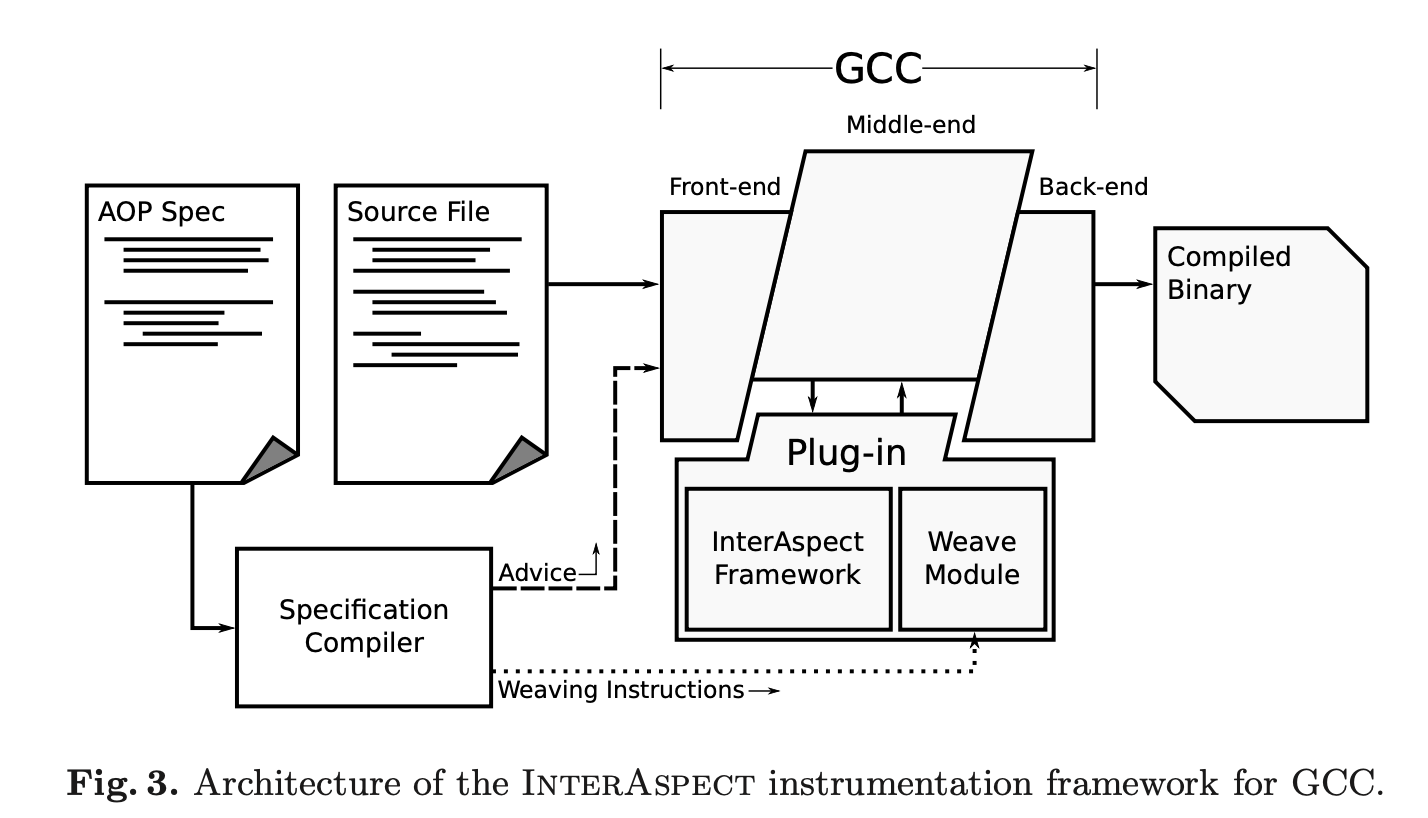
Poincuts are retrieved and refined using a set of C API. i.e. Can match function call, function exit, variable assignment, and filter them either by name or by type.
The aop_join_on function
associates each pointcut with a callback function.
The callback function inspects each join point and decide whether/where to insert advice function.
Limitations
GIMPLE does not reveal the high-level constructs in source languages. The pointcut API may be extended to inspect AST.
Not all AspectJ pointcut refinements are supported. Maybe they can be added later.
Case studies
Heap visualization

Code Coverage

Related Works
- AOP originated from AspectJ for Java
- JVM bytecode editing API: Javaassist and PROSE.
- AspectJ knockoffs for C and C++: AspectC/C++
- XWeaver: XML and XPath based AOP for Java and C++